本帖最后由 荷花池荒岛 于 2015-11-30 06:46 编辑
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) and Its Receptor (VEGFR) Signaling in Angiogenesis
血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)及其受体(VEGFR)在血管生成中的信号传输
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3411125/
Abstract
The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptor (VEGFR) have been shown to play major roles not only in physiological but also in most pathological angiogenesis, such as cancer. VEGF belongs to the PDGF supergene family characterized by 8 conserved cysteines and functions as a homodimer structure. VEGF-A regulates angiogenesis and vascular permeability by activating 2 receptors, VEGFR-1 (Flt-1) and VEGFR-2 (KDR/Flk1 in mice). On the other hand, VEGF-C/VEGF-D and their receptor, VEGFR-3 (Flt-4), mainly regulate lymphangiogenesis. The VEGF family includes other interesting variants, one of which is the virally encoded VEGF-E and another is specifically expressed in the venom of the habu snake (Trimeresurus flavoviridis). VEGFRs are distantly related to the PDGFR family; however, they are unique with respect to their structure and signaling system. Unlike members of the PDGFR family that strongly stimulate the PI3K-Akt pathway toward cell proliferation, VEGFR-2, the major signal transducer for angiogenesis, preferentially utilizes the PLCγ-PKC-MAPK pathway for signaling. The VEGF-VEGFR system is an important target for anti-angiogenic therapy in cancer and is also an attractive system for pro-angiogenic therapy in the treatment of neuronal degeneration and ischemic diseases.
摘要
血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)和它的受体(VEGFR)已经被证明不仅在生理而且在大多数病理性血管新生,如癌症,起到了主要作用。 VEGF属于PDGF超基因家族并且作为一个同二聚体结构发挥功能。PDGF超基因家族特征是8个保守的半胱氨酸。VEGF-A通过激活2受体,VEGFR-1(受体Flt-1)和VEGFR-2(KDR / Flk1的小鼠)调节血管新生和血管通透性。另一方面,VEGF-C / VEGF-D和它们的受体,VEGFR-3(FLT-4),主要调控淋巴管生成。 VEGF家族包括其他有趣的变体,其中一个是携带有病毒编码的VEGF-E以及另外一个只在羽生蛇(竹叶青flavoviridis)的毒液中特异性表达。 VEGFRs是远亲的PDGFR家庭;但是它们具有独特的结构和信号系统。不像PDGFR家族的成员那样在细胞增殖中强烈刺激PI3K-Akt通路,VEGFR-2,血管生成中的主要信号转导,优选利用PLCγ-PKC-MAPK途径用于信号传输。VEGF-VEGFR系统是癌症的抗血管生成治疗的一个重要目标,同时对于促血管发生治疗中的神经元变性和局部缺血性疾病的治疗也是一个有吸引力的系统。
Introduction
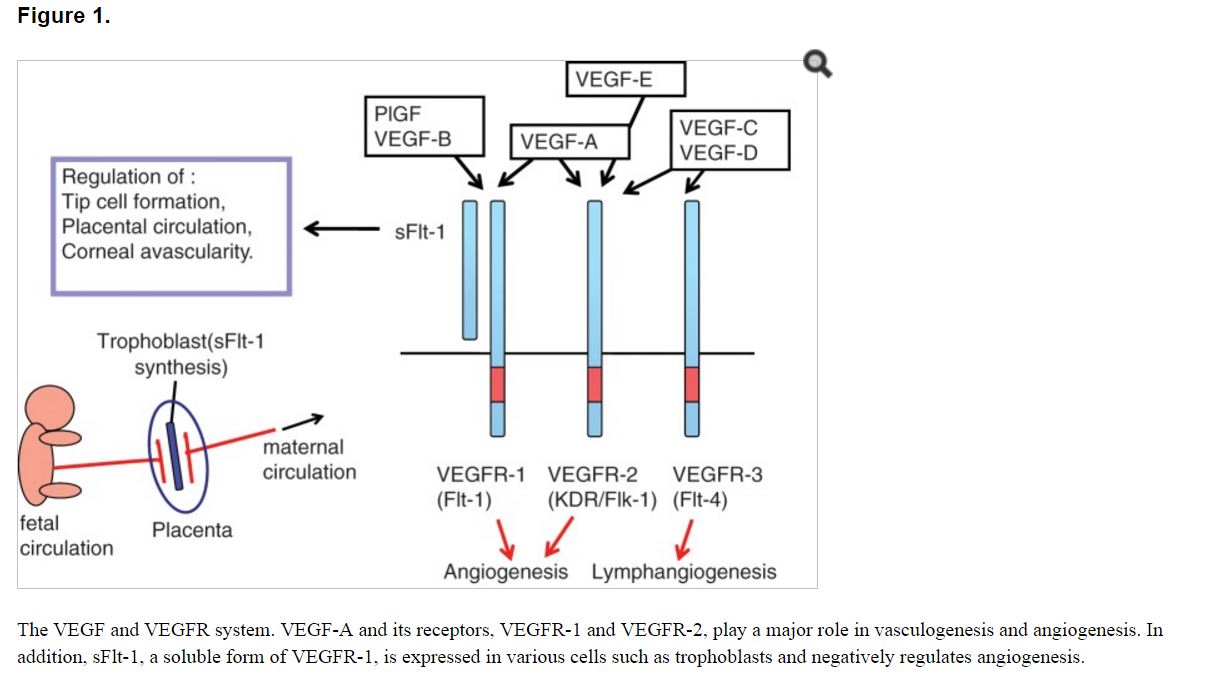
Angiogenesis, the formation and maintenance of blood vessel structures, is essential for the physiological functions of tissues and is important for the progression of diseases such as cancer and inflammation. In recent decades, a variety of signaling molecules, such as VEGF-VEGFRs, ephrin-Eph receptors, angiopoietin-Tie, and the Delta-Notch system, have been identified as playing important roles in angiogenesis. Among these, vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs) and receptors (VEGFRs) regulate both vasculogenesis, the development of blood vessels from precursor cells during early embryogenesis, and angiogenesis, the formation of blood vessels from pre-existing vessels at a later stage3 (Fig. 1). The VEGF family of genes contains at least 7 members, including the viral genome–derived VEGF-E, whereas the VEGFR family of genes has 3 to 4 members depending on the vertebrate species. VEGF-A and its receptors VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 play major roles in physiological as well as pathological angiogenesis, including tumor angiogenesis. VEGF-C/D and their receptor VEGFR-3 can regulate angiogenesis at early embryogenesis but mostly function as critical regulators of lymphangiogenesis.
引言
血管新生,即血管结构的形成和维持,对于组织的生理功能是必不可少的,并且对于例如癌症和炎症的疾病的进展也是重要的. 近几十年来,各种信号分子,如VEGF-VEGFRs,ephrin-Eph受体,angiopoietin-Tie,和Delta-Notch系统,已被确定为在血管新生中发挥重要作用。其中,血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)和受体(VEGFRs)既调节了在胚胎发育早期由前体细胞发展而来的血管形成(vasculogenesis),又调节了在后一阶段由既存管腔形成血管的血管新生(angiogenesis)(图1)。基因的血管内皮生长因子家族包含至少7名成员,其中包括病毒基因组衍生的VEGF-E,而VEGFR基因家族根据脊椎动物种类的不同有3到4个成员。 VEGF-A及其受体VEGFR-1和VEGFR-2对生理上以及病理性血管新生,包括肿瘤血管新生,发挥了主要作用。 VEGF-C / D及其受体VEGFR-3能够在早期胚胎发育过程中调节血管形成,但主要作为淋巴管生成的关键调控者发挥作用。
VEGF-A has a variety of functions, including pro-angiogenic activity, vascular permeability activity, and the stimulation of cell migration in macrophage lineage and endothelial cells. Recently, anti–VEGF-VEGFR drugs such as an anti–VEGF-A neutralizing antibody and multikinase inhibitors have been developed and widely used for the treatment of major solid tumors.7,8 The clinical efficacy of these medicines has been well evaluated; however, none of them provide a complete cure for cancer patients. The molecular basis of the refractoriness in some tumors and the acquisition of resistance to these medicines should be extensively studied to develop more efficient anti-angiogenic therapies.
VEGF-A具有多种功能,包括促血管生成活性,血管通透性的活性,和刺激巨噬细胞谱系细胞和内皮细胞内的细胞迁移。近来,抗VEGF-VEGFR药物如抗VEGF-A的中和抗体和多激酶抑制剂已经被开发并广泛用于主要实体肿瘤.。这些药物的临床疗效已经被深入地评估;不过,没有一种药物可以完全地治愈癌症患者。某些肿瘤中对药物具有的抵抗性分子基础和对药物获取性耐药的分子基础应该广泛地研究以开发更有效的抗血管生成疗法。
On the other hand, VEGFs have pro-angiogenic potential for the maintenance of various tissues at physiological levels and for the formation of new blood vessels to overcome ischemic diseases. The utility of VEGF family members in pro-angiogenic medicine, together with the possible side effects, should be characterized in more detail for clinical applications.
另一方面,对于不同组织在生理水平上的维持以及形成新的血管以克服缺血性疾病而言,VEGF具有促进血管发生的潜能。VEGF家族成员在促血管生成药物中的效用,以及可能的副作用,应该更详细地描述以用于临床应用。
Structure and Function of the VEGF Family
VEGF家族的结构与功能
VEGF, also known as VEGF-A, is a protein with vascular permeability activity that was originally purified from a fluid secreted by a tumor. A few years later, a protein with angiogenic activity was independently purified and named VEGF. Molecular cloning, however, revealed that these 2 proteins were identical and encoded by a single gene. The VEGF family includes VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C, VEGF-D, PlGF (placental growth factor), VEGF-E (Orf-VEGF), and Trimeresurus flavoviridis svVEGF. With the exception of the latter 2 members, 5 genes of the VEGF family exist in mammalian genomes, including humans. Essentially, all the VEGFs have 8 conserved cysteine residues at fixed positions, which are very similar to the PDGF family such as M-CSF (CSF-1), SCF (stem cell factor), and Flt3L (Flt3 ligand). Among the 8 cysteines, 6 residues form 3 S-S intramolecular bonds and generate 3 loop structures. The remaining 2 cysteines form 2 S-S intermolecular bonds, contributing to the stable homodimer structure of VEGF. We have shown that a structure combined with loop 1 and loop 3 in VEGF-A and VEGF-E is essential for the binding and activation of VEGFR-2.
VEGF,也被称为VEGF-A,是一个最初从由肿瘤分泌的流体纯化而来的具有血管通透性活性的蛋白。几年后,一个具有血管生成活性的蛋白质被独立纯化并被命名为VEGF。分子克隆却揭示了这两个蛋白是完全一样的,并且由单个基因编码。 VEGF家族包括VEGF-A,VEGF-B,VEGF-C,VEGF-D,PlGF(胎盘生长因子),VEGF-E(ORF-VEGF)和竹叶青 svVEGF。除了最后两个成员,VEGF家族的5个成员存在于包括人类在内的哺乳动物基因组。本质上,所有VEGF家族成员具有8个在固定位置上的保守的半胱氨酸残基,这是PDGF家族如M-CSF(CSF-1),SCF(干细胞因子),和FLT3L(Flt3配体)非常相似。8个半胱氨酸中,6个残基形成3个SS分子内键并产生了3个循环结构。剩余的2个半胱氨酸形成2个SS分子间键,促进VEGF的同型二聚体结构的稳定性。我们已经表明一个结合了VEGF-A和VEGF-E中的环1和环3的结构对于VEGFR-2的结合和活化是必需的。
注一:关于angiogenesis 和 vasculogenesis的翻译,参考:
http://www.dxy.cn/bbs/thread/25501128#25501128
http://www.dxy.cn/bbs/topic/19300780?keywords=vasculogenesis
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15015550
http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KJSY200704021.htm
|